Endoscopy was devised as a method of viewing and operating inside the body while requiring minimum invasive procedures and incisions, thus allowing for a much faster recovery and avoidance of large scars. After making a small incision, the surgeon inserts an endoscope, a flexible tube with an attached camera, inside the incision where the organs or blood vessels must be operated upon.
Sometimes, the purpose of endoscopy is diagnostic. In that case, the endoscope can be inserted through the mouth, nose, vagina, urethra, or rectum, depending on which body organ needs to be visually examined.
Common Endoscopy Uses
Only some doctors can perform endoscopy. It requires unique and vigorous training. After all, inserting a foreign object inside a body and delicately manipulating it is not simple. The doctor has to handle the endoscope with high precision as if it were the extension of his hand, not to mention the in-depth knowledge of anatomy.
Nonetheless, compared to regular surgical procedures, endoscopy is considered to be exceedingly safe. Gastroenterologists, preferably using top-of-the-line equipment, such as Pentax EG 1690K Gastroscope, which has an ergonomic design, easy handling, and integrated image sensors, perform most endoscopy procedures.
Endoscopy is called for in any diagnostic situation when there’s a suspicion of infection, damage, or cancer on any part of your body, which cannot be conclusively determined through other methods such as physical examination, symptom deduction, or bloodwork. The most common uses for endoscopy are related to stomach pain, ulcers, gastritis, chronic constipation, polyps, and swallowing difficulty, as well as for biopsy purposes.
When surgery is needed, it’s always better to make it the least invasive. Unfortunately, not many surgeons specialize in endoscopic surgeries, and many situations require quick response, which leaves little room for endoscopic surgical intervention.
Importance of State of the Art Equipment
Over the years, endoscopic video technology has advanced significantly, not just for medical practice but also for veterinary usage and other specialized industries where there’s a need for highly cost-effective and non-destructive material testing and maintenance. At the forefront of video endoscopy development is H.M.B. Endoscopy Products, situated in Hollywood, Florida.
Over the past 17 years, they have been developing new endoscopic systems and equipment and educating people on their proper use. Their older model, Karl Storz SCB Image 1 HUB HD, remains the endoscopic mainstay in many hospitals and clinics nationwide. Its full HD resolution and progressive scan ensure a lag-free image and accurate color reproduction.
Nowadays, most video endoscopes are set up with a coupler, which enables compatibility with almost all standard endoscopes and rigid borescopes.
What is Video Endoscopy Equipment?
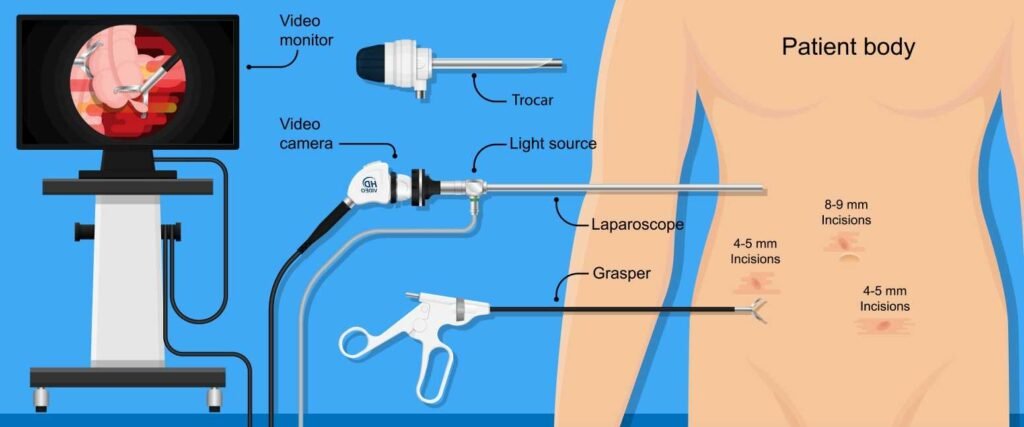
Endoscope Video Processors is a long, thin tube that is inserted into the body via the esophagus or anus to detect the internal organs of the body. Endoscopy is usually done in conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease to check cancer of the esophagus or perform colonoscopies.
There are vast varieties of endoscopic devices that professionals use to perform laparoscopy, colonoscopy, and many others. These devices allow the doctor to take the sample from the patient’s body and send it for biopsy.
These tests are generally used when cancer is suspected. Some useful endoscopic devices are:
- Biopsy forceps
- Cleaning brushes
- Ligation devices
- Tissue scissors and cutters
- Tube sets
- Tissue staplers
The endoscope is the camera that visualizes the digestive and genitourinary tracts. Equipment consists of the following components-
- Tube: either it may be rigid or flexible.
- Light: the light source is outside the body and directs light via an optical fiber. The light system allows accurate visualization.
- Lens system: this is the most important equipment as it transmits the light from the internal end of the endoscope to the viewer.
- Modern endoscopes have display screens instead of eyepieces, thus providing the best view as organs can be visualized on larger screens.
- Additional channels: through the endoscope, other instruments can be quickly passed into the body.
Where to use endoscopes?
The gastrointestinal tract will visualize the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. Thus, colonoscopies and laparoscopies are done using endoscopy equipment.
- Ear- Otoscopes visualize the ear and its detailed examination.
- Respiratory tract- Rhinoscopy and bronchoscopy are performed to detect bronchial carcinoma, and the extracted material is sent for biopsy.
- Urinary tract- cystoscopy is done to detect mild inflammation or cystitis.
- The gyroscope is done to visualize the female genital tract, such as colposcopy for the cervix, hysteroscopy for the uterus, and fluoroscopy for the fallopian tubes.
Why do the endoscopy?
Endoscopy is an investigation performed to detect the cause of illness. Like others, endoscopy investigations hold great importance in present-day techniques. If a person is experiencing vomiting, abdominal pain, stomach ulcers, persistent acidity (gastroesophageal reflux disease), or difficulty swallowing, an endoscopy is performed.
Endoscopies can be used for the detection of cancer, as a biopsy requires tissue from the particular organ that is suspected.
With the advancement of technology, modern endoscopes are incorporated with sensitive lights that use “narrow band imaging” for visualization. This allows for detecting a precancerous condition that uses green and blue wavelengths and, hence, is a vital tool for cancer diagnosis.
Preparation of an endoscopy
Endoscopy is performed when a patient is conscious or has received a local anesthetic. While inserting the tube through the mouth, a mouth guard is applied to prevent tube biting. The guard will protect the teeth and lips while the procedure continues. The patient can not drink or eat food before the endoscopy proceedings.
What can an Endoscopy diagnose?
You may be apprehensive about going for it if you suffer from digestive issues—a medical checkup. The thought of tubes sticking in your body or X-rays and syringes can put you off from seeing sounds like you; you may be encouraged to find an alternative method of checking internal body issues—endoscopy diagnosis.
Tools used during endoscopy
Endoscopy tubes usually have channels through which the doctor introduces tools that collect tissue or treat infected areas. These tools can include:
- Biopsy forceps – these remove suspicious growths or tissue samples
- Forceps – are flexible and used to take tissue samples
- Suture removal forceps – to remove possible stitches in the body
- Cytology brush – this removes cell samples
Types of endoscopy
Doctors investigate several body areas through endoscopy. It gives rise to several types, which are:
Gastrointestinal
- Stomach, esophagus, duodenum – esophagogastroduodenoscopy, or upper GI endoscopy.
- Colon/large intestine – colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy
- Small intestine – enteroscopy
- Rectum and bile duct – rectoscope
- Anus – anoscopy
Ear
Otoscopy
Respiratory system
- Lower respiratory tract – bronchoscopy
- Nose – rhinoscopy
- Larynx/voice box – laryngoscopy
Female reproductive system
- Uterus – hysteroscopy
- Cervix and the vagina – colposcopy
- Fallopian tubes – fluoroscopy
Urinary tract
Cystoscopy
Minor incisions
- Chest organs and lungs – mediastinoscopy, thoracoscopy
- Pelvic or abdominal cavity – laparoscopy
- Stomach, liver, or other abdominal organs, including reproductive systems – Laparoscopy
- Joint interiors – arthroscopy
- Brain – neuroendoscopy
Why you should do an endoscopy
Apart from digestive issues in your body, doctors can also recommend endoscopy diagnosis to investigate:
- Difficulties in swallowing, ulcers, or gastritis
- Stomach pains
- Bleeding in the digestive tract
- Polyps (growths) in the colon and colon cancer detection
- Biopsies (tissue removal) to look for the presence of diseases
- Issues with your internal organs, including reproductive and respiratory systems
- Removal of gallstones that are in your bile duct
What are some things that an endoscopy can identify?
The most common use of endoscopy procedures is to isolate the causes of digestive problems such as nausea, abdominal pain, bleeding, swallowing issues, and heartburn. It can also identify ulcers, inflammation, and tumors.
You can undergo treatment for abnormal growths using this procedure, for example:
- Removal of objects that are stuck in the esophagus or stomach
- Removal of tissue sample (biopsy) as well as treatment of polyps (abnormal tissue growth in the stomach)
- Treatment of bleeding from ulcers.
If you have criticisms or narrowed areas of your duodenum, stomach, or esophagus because of cancer or other diseases, they can be stretched (dilated) using balloons or tubes. If the complication is severe, the doctor can use a wire or plastic mesh (stent) to open the stricture.
Upper GI endoscopy can also detect conditions such as:
Barrett’s Oesophagus and GERD (Gastrointestinal reflux disease)
GERD happens when acid from the stomach – gastric acid – flows into the esophagus. This acid can burn and damage the esophagus lining and leads to the development of Barrett’s esophagus, a condition of abnormal cell growth leading to cancer.
If you have long-term symptoms of GERD, your doctor can order an upper GI endoscopy for you. These symptoms include nausea, indigestion, heartburn, and vomiting. The doctor performs the endoscopy diagnosis using a light that spots abnormal tissue and then takes a biopsy. A pathology lab can then know if the cells are abnormal.
Tumors and cancer
Your doctor can do an endoscopy through biopsies to diagnose abnormal bumps, ulceration, and swellings. The biopsy is examined in a pathology lab to know if it is malignant (cancerous) or benign (non-cancerous). Stomach or gastric cancer is the most common cancer of the upper intestinal tract, then oesophageal cancer, while the cancer of the duodenum is rare.
If you have risk factors or symptoms of upper GI cancer, you can undergo an endoscopy. The risk factors can include family histories of cancer or long-term gastritis. The symptoms can include anemia, nausea, swallowing pain, and vomiting.
Ulcers and inflammation
Inflammation of the digestive tract can include duodenum inflammation (duodenitis), stomach inflammation (gastritis), and esophagus inflammation (esophagitis). Usually, ulcers are caused by inflammation due to the erosion of the wall linings through Helicobacter pylori infections. The infections may lead to stomach–peptic and duodenal ulcers.
Typical symptoms of ulcers include burning stomach pain, bloating, nausea and vomiting, and belching.
Oesophageal strictures
Oesophageal strictures are narrowings of the esophagus that can block the passage of liquids and food into the stomach. Large food pieces can even be stuck. The symptoms of this condition include difficult and painful swallowing, shortness of breath, chest pressure or pain, and vomiting.
Esophageal varices
These are enlarged veins or blood vessels in the esophagus walls that can rupture (burst) and bleed. The main signs of varices are vomiting and passing bloody or black stool, which needs quick treatment as the loss of blood is life-threatening.
A significant risk for varices is liver disease, so your doctor may order an upper GI endoscopy if you have a case of liver disease. If there is active bleeding, you will undergo an emergency procedure.
Endoscopy Camera Systems for Medical Professionals
Endoscopy cameras are crucial for medical diagnostics and surgeries, providing high-definition visuals of the body’s interior. These systems perform minimally invasive procedures, enhancing surgery’s accuracy and success rates.
1. KARL STORZ IMAGE1 S ($12,999)
Features:
This system offers high-resolution images and videos in real-time, making it easier for surgeons to make precise movements during procedures. It’s modular, allowing customization to suit different surgical needs, including 3D visualization. The system also supports various illumination modes (e.g., NBI – Narrow Band Imaging) to enhance the visibility of vascular structures and mucosal textures.
Advantages:
The IMAGE1 S’s flexibility and modular design suit various surgical specialties, including urology, gynecology, and general surgery. Its advanced imaging technologies provide exceptional clarity, contrast, and detail, aiding in accurate diagnostics and surgical precision.
2. Olympus VISERA ELITE III ($38,950.00)

In the ever-evolving field of medical technology, the VISERA ELITE III stands out as a pioneering surgical visualization system designed to enhance the precision and effectiveness of various surgical procedures. As a leading healthcare provider, we are proud to incorporate this advanced technology into our practice, offering our patients the highest standard of care.
Key Features of VISERA ELITE III:
- Enhanced Visualization: With its state-of-the-art high-definition imaging capabilities, VISERA ELITE III provides surgeons with crystal clear, detailed views of the surgical area, enabling more accurate and precise interventions.
- Ergonomic Design: The system is engineered for optimal usability, ensuring that surgeons can maintain comfort and focus during long procedures.
- Versatility: Ideal for a wide range of surgical specialties, including general surgery, urology, and gynecology, VISERA ELITE III adapts to various medical needs and procedures.
- Integrated Functionality: Seamless integration with other surgical equipment and systems allows for a streamlined workflow and enhances overall efficiency in the operating room.
Benefits of Using VISERA ELITE III:
- Improved Surgical Outcomes: By providing superior visualization, VISERA ELITE III helps in reducing the risk of complications and improves the precision of surgical interventions.
- Shorter Recovery Times: Enhanced precision and reduced invasiveness lead to quicker recovery times for patients.
- Increased Patient Safety: The system’s advanced features ensure a higher level of control and safety during operations, contributing to better patient outcomes.
Conclusion:
The VISERA ELITE III is more than just a piece of equipment; it’s a vital part of our commitment to providing exceptional surgical care. With its advanced capabilities, we are equipped to handle the most challenging medical cases with precision and confidence. Contact us today to learn more about how our state-of-the-art surgical solutions can help you or your loved ones.
3. Stryker 1688 AIM 4K Camera ($11,780.00)

Features:
This camera system boasts 4K Ultra HD resolution, providing four times the resolution of HD cameras for unmatched clarity and detail. It features advanced imaging modalities like fluorescence imaging to highlight critical anatomical structures.
Advantages:
The 4K resolution significantly enhances the surgeon’s ability to see fine details, improving surgical outcomes. The addition of fluorescence imaging is a significant advantage in complex surgeries, aiding in the precise identification of tissues and ensuring surgical accuracy.
Conclusion
When you undergo an endoscopy diagnosis, you do not need primary surgical operations that carry risks, such as extended healing periods. Despite this, endoscopy carries short-term inherent risks, such as feeling bloated after the procedure, mild cramps, or dry throat. If you have persistent symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, it is best to consult your doctor.
One Reply to “Video Endoscopy Equipment: A Doctor’s Guide for Medical Practices”
Finding The Best Endoscope Video Processors | Ferus Medical
[…] article will explore the science and technology behind video endoscopy. We will also highlight some of the best options available to […]